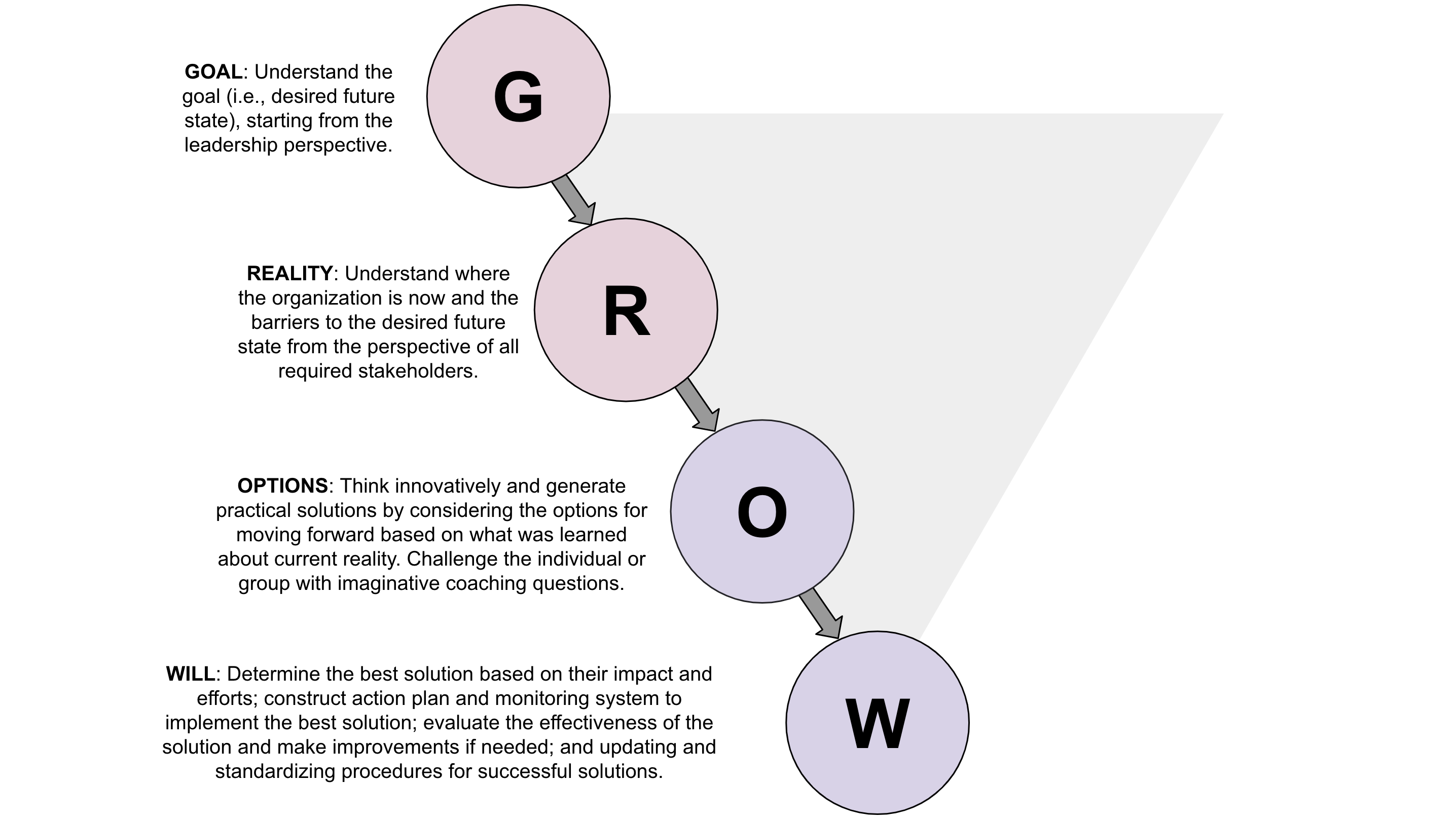
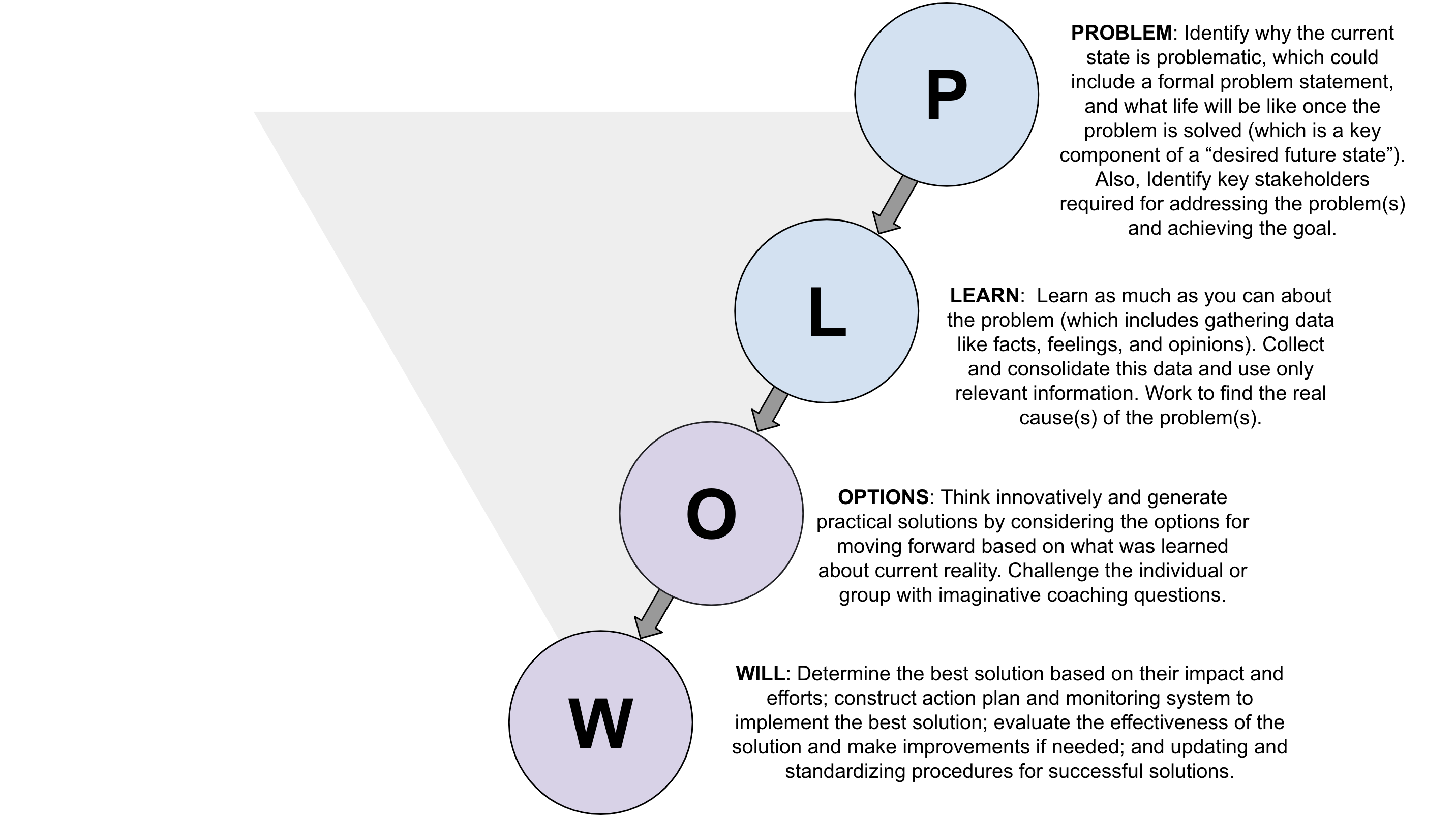
One of the conditions of a Team is continuous coaching. This is to enable the team to become high-performing and well functioning. Without putting time and effort into team coaching it is very hard to become high-performing as a team, and most teams need experts to support in the beginning to move beyond friction and into the phase of the structure.
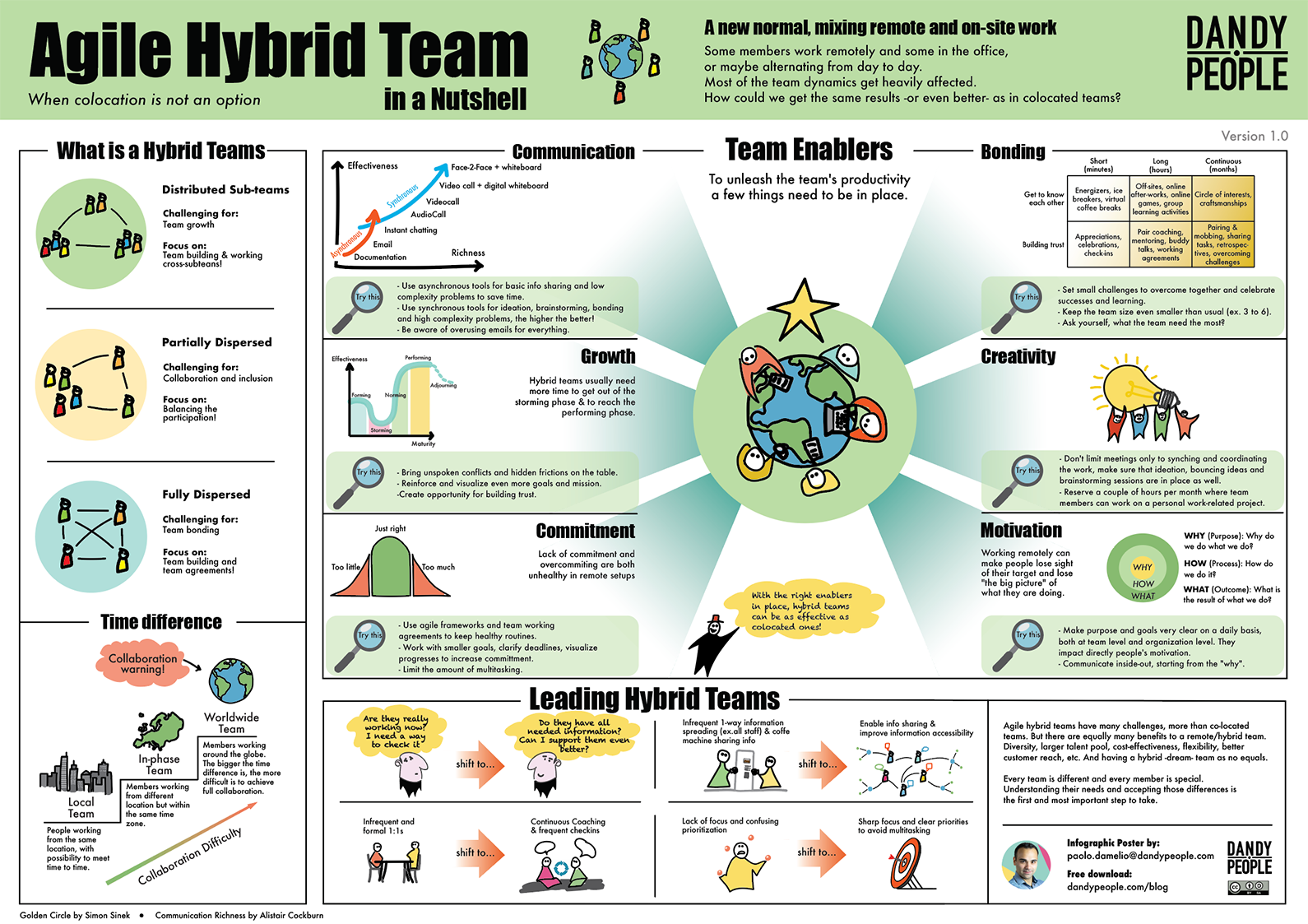
The 5 Stages of a Team

1. Inclusion
The team meets and learns about the work that needs to be done and what’s expected of them. Members avoid disagreement because they fear rejection at this stage, making the leader a central role providing
direction. There is a desire for order, roles, and structure.
The need of the team: All team members understand the purpose of the team and want to be part of it. Team members know and accept each other and feel accepted as a member of the team.
The leaders role: Provide structure. Make sure everyone is included. Initiate open discussions of values & goals.
Common leadership pitfalls: Analysis paralysis / Not daring to make decisions. Thinking the leader need to have all answers.
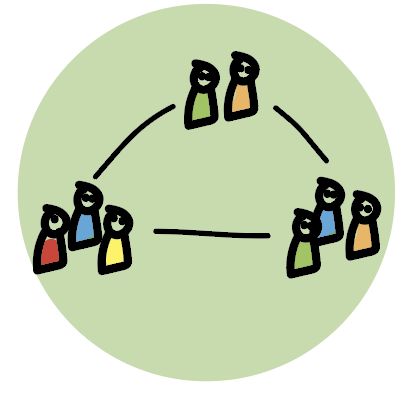
2. Friction
The team starts challenging the defined boundaries, such as process and working agreements and voice differences in individual working styles and behaviors. Team members challenge each other. Some question the team’s goals altogether. Typically, this will be a challenging phase.
The need of the team: Understanding of each other’s behavioral style and intention. Improved ability to resolve disagreement effectively.
The leaders role: Support, coach & train the team in how to keep an open dialogue. Help solve conflicts. Build trust.
Common leadership pitfalls: Picking on individuals – stay focused on ideas, not personalities. A leader that’s unwilling to compromise. A belief that the team needs conflict to advance from this stage – allow disagreement but don’t foster conflict.
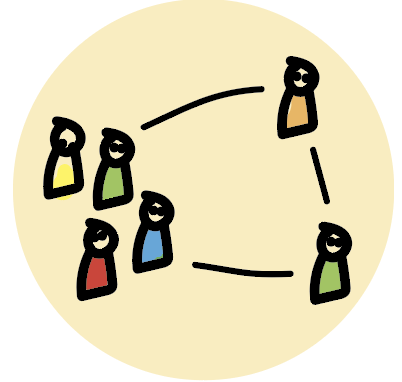
3. Structure
The team has the ability to resolve disagreement and integrates their personal differences. They revisit goals and objectives and redefine structures, working agreements, roles, and processes to support them.
The need of the team: Time to work out structures within the team such as processes, goals, roles, and working agreements. Everyone feels that issues regarding ways of working that are important to them have been discussed.
The leaders role: Act as consultants when needed. Support by removing impediments outside of the team.
Common leadership pitfalls: Not taking the time to make sure everyone’s perspective is represented. Trying to get everyone to conform to the same values. Trying to find the perfect solution.
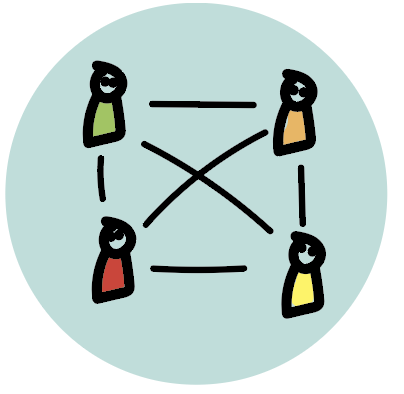
4. Performing
The team have agreement on goals and objectives and work towards them together. The team is competent in decision making and conflict resolution with minimal or no supervision. The team rapidly gains important knowledge through knowledge sharing – there’s no information hoarding. Relationships and results are equally important.
The need of the team: The team is self-managed and continuously evaluate their own performance.
The leaders role: Share responsibilities with the team. Reward initiative. Coach & facilitate individual development.
Leadership pitfalls: Expecting to not have to further improve and still maintaining high performance.
(more…)